VS Code with devcontainers ¶
Info
VS Code with Devcontainers is the recommended development setup
Warning
You must build the base Docker image benefits_client:latest before running the devcontainer.
See Local Setup
Install the Remote - Containers extension ¶
VS Code can be used together with Docker via the Remote - Containers extension to enable a
container-based development environment. This repository includes a .devcontainer.json file that configures
remote container development and debugging.
Open the repository with VS Code ¶
With the Remote - Containers extension enabled, open the folder containing this repository inside Visual Studio Code.
You should receive a prompt in the Visual Studio Code window; click Reopen in Container to run the development environment
inside a container.
If you do not receive a prompt, or when you feel like starting from a fresh environment:
- Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P to bring up the command palette in Visual Studio Code
- Type
Remote-Containersto filter the commands - Select
Rebuild and Reopen in Containerto completely rebuild the devcontainer - Select
Reopen in Containerto reopen the most recent devcontainer build
Attach a debugger ¶
Once running inside a container, press F5 to attach a debugger to the client, running on http://localhost at a port
dynamically assigned by Docker. See Docker dynamic ports for more information.
Add breakpoints in the code and browse the local site to trigger a pause. Press F5 to continue execution from the breakpoint.
Changing launch configuration ¶
By default, the application is launched with DJANGO_DEBUG=True, causing Django to provide additional logging and error output and to relax certain security settings.
Alternatively, you may attach to an instance launched with DJANGO_DEBUG=False, to allow debugging the app in a state more similar to production.
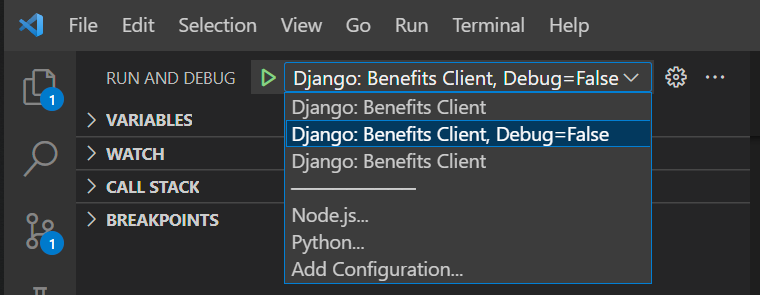
In VS Code, press Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + D to open the Run and Debug pane, where you can select between the various configurations (disregard the duplicate entry, selecting either will work):
The environment can also be overridden for the debug session by editing the configuration in .vscode/launch.json, where any of the supported environment variables may be specified in the env block. For example, to test the app with reCAPTCHA environment variables:
{
"name": "Django: Benefits Client",
"type": "python",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/manage.py",
"args": ["runserver", "--insecure", "0.0.0.0:8000"],
"django": true,
"env": {
// existing field...
"DJANGO_DEBUG": "true",
// add these 2 entries with the values for reCAPTCHA
"DJANGO_RECAPTCHA_SITE_KEY": "<SITE KEY HERE>",
"DJANGO_RECAPTCHA_SECRET_KEY": "<SECRET KEY HERE>"
}
}
See #1071 for more examples and context.
Exiting devcontainers ¶
To close out of the container and re-open the directory locally in Visual Studio Code:
- Ctrl/Cmd + Shift + P to bring up the command palette in Visual Studio Code
- Type
Remote-Containersto filter the commands - Select
Reopen Locally